What Is Depth Perception & How Does It Work?
Picking a cup of coffee up from a counter without knocking everything else – seems like a simple enough task, right?
In reality, it’s actually the result of good depth perception, which is a pretty sophisticated visual process involving the coordination of your eyes and hands.
Without depth perception, our lives would look quite different. For starters, you wouldn’t be able to drive safely, and sports would be even more complex than they already are, among others. Let’s dive into how depth perception works.
What is depth perception?
The ability to see things in 3D and judge distances is depth perception in action. When we look around, light rays enter the pupil and land on the retina. There, these rays form two-dimensional images that are sent to the brain for processing. The brain then interprets these images as a three-dimensional representation of the world around us.
In addition to that, the brain uses different cues to understand how far away things are and how they are positioned in space. These clues are called binocular, monocular, and oculomotor cues.
What are binocular cues?
Binocular cues are visual cues that involve the use of both eyes to perceive depth and distance. These cues include retinal disparity, the difference in the images that each eye sees, and convergence, which is the inward movement of the eyes as they focus on an object at a close distance. These cues are important for depth perception and spatial awareness.
What are monocular cues?
Monocular cues rely on the use of one eye to perceive depth, or techniques to create depth, motion, and spatial relationships in an image. These include relative size, relative height, relative motion, linear perspective, and texture gradient.
Relative size represents objects’ sizes in proportion to each other, while relative height represents objects’ height relative to each other. Relative motion creates a sense of movement in an image.
Linear perspective creates the illusion of depth and three-dimensionality by using objects’ and viewer’s relationship. Texture gradient creates a sense of depth by gradually changing the texture or surface quality in an image.
What are oculomotor cues?
Oculomotor cues, such as convergence and accommodation, are visual cues related to the movement of the eyes. The brain uses these cues, along with the change of size and motion as the eye moves, to determine perception of depth.
How does poor depth perception affect us?
Having poor depth perception can affect a person’s ability to judge distances and perceive the three-dimensional structure of objects. This can make driving, sports, and even walking difficult. It can also make judging the size and shape of objects challenging.
Depth perception issues for adults
For adults, poor depth perception can lead to difficulties with tasks requiring fine motor coordination such as threading a needle, or spatial tasks such as navigating unfamiliar spaces or driving.
It could also endanger those with jobs that require spatial awareness, such as pilots, crane operators, and architects.
Underlying conditions like crossed eyes or lazy eye can lead to poor depth perception. This may lead to double vision or difficulty seeing 3D objects, so do seek treatment if you have any of these conditions.
Depth perception issues for children
Children with poor depth perception may have trouble with tasks requiring fine motor coordination, like holding a pen for writing or drawing, and judging distances. This can make climbing, playing on playground equipment, and even walking difficult for them. It can also affect their school abilities, as it can make reading and mathematical tasks more tricky.
In worse cases, poor depth perception in children presents a safety hazard as it increases the likelihood of accidents.
4 ways to test your depth perception
1. At-home method of testing
Several methods can be done at home to determine if an individual has a problem with depth perception. Credit to Research Gate:
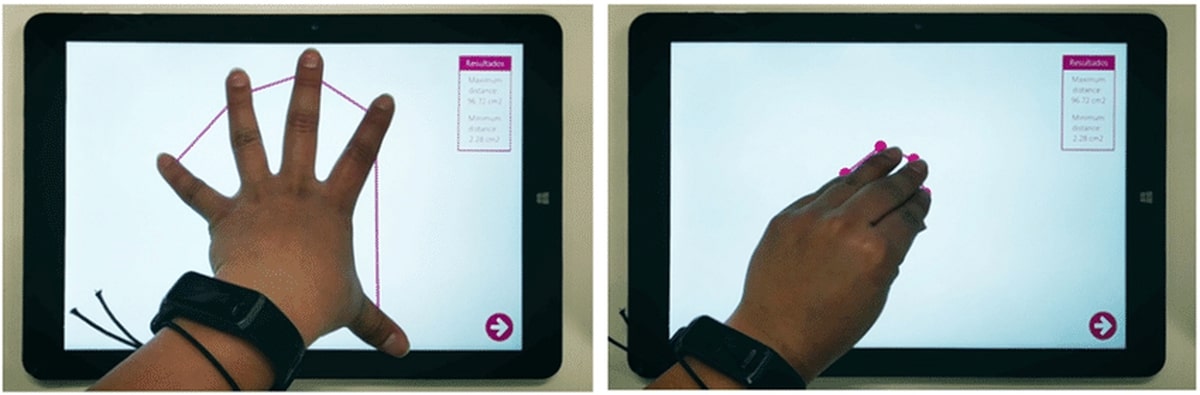
- TappingTapping with one finger (left) and tapping with each finger while the remaining digits are weight-bearing (right).
- Pincer graspMaximum (left) and minimum pincer (right).
- Hand opening and closingMaximum opening (left) and closing (right).
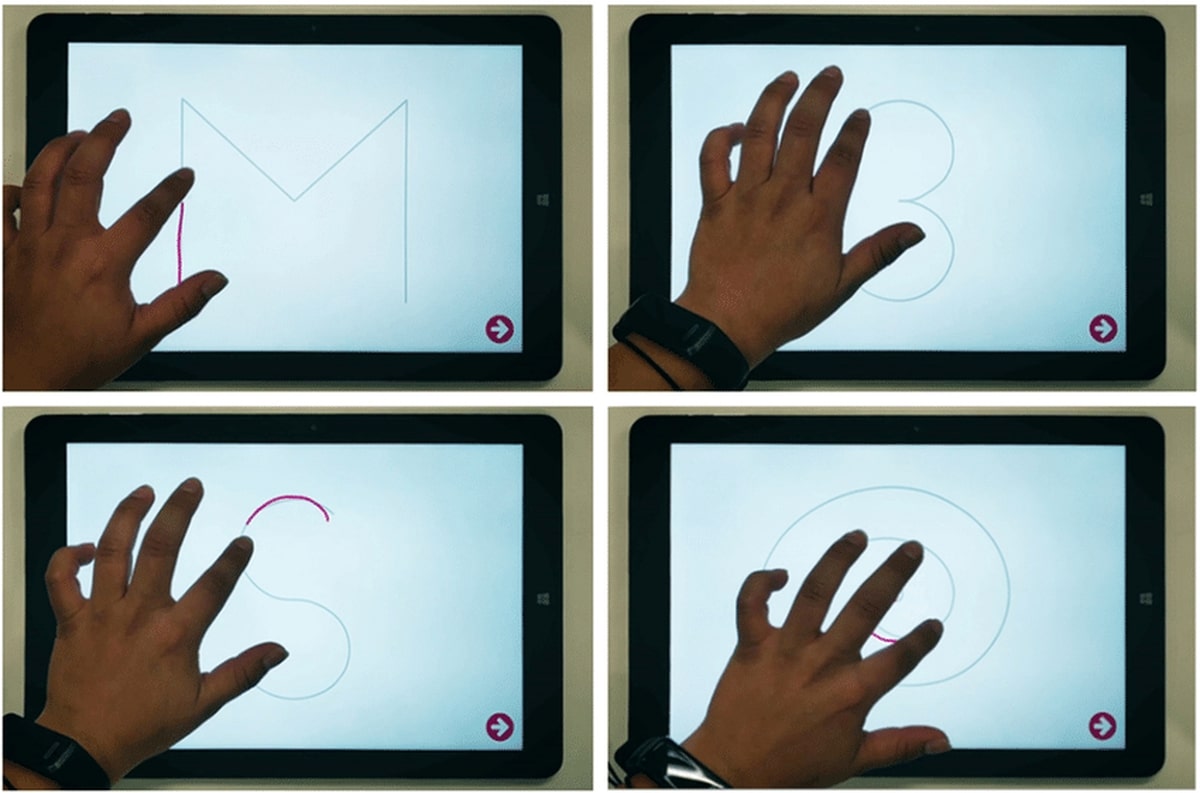
- GraphomotricityDrawing an M (top-left), a 3 (top-right), an S (bottom-left), and a spiral (bottom-right).
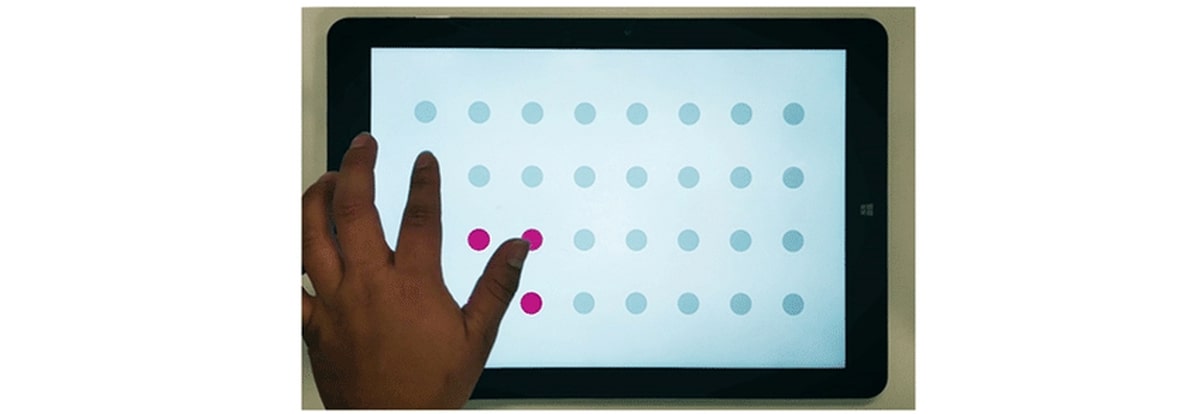
- Oculo-manual coordinationUsing the eyes to track and fingers to tap on the moving pink dots.
Hand-eye coordination and finger-thumb tests are commonly used to evaluate an individual’s ability to judge distances and coordinate their eyes and hands.
Meanwhile, the hole-in-the-card test is used to determine if someone has difficulties perceiving depth in 2D images or judging distances.
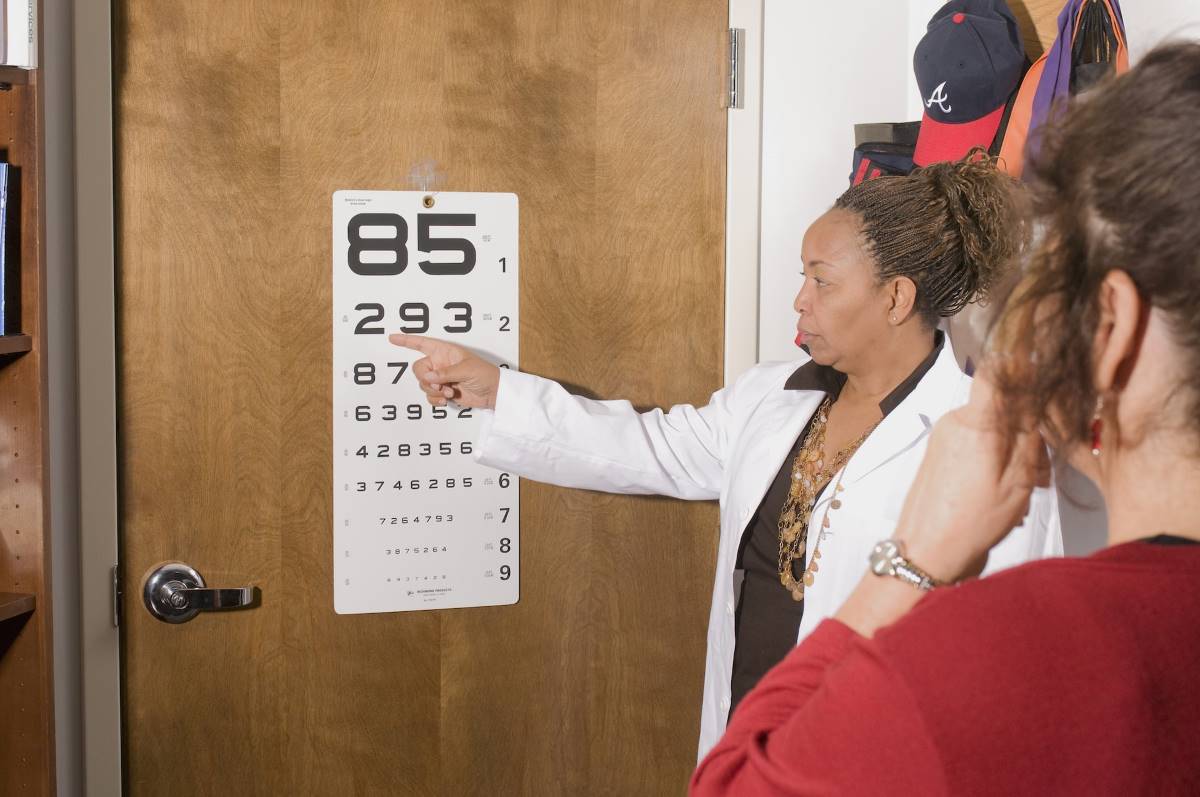
2. Testing your depth perception at an eye exam
An eye doctor can use various tests to assess a person’s depth perception, with the standard one being the Snellen chart. It’s a test that involves reading smaller letters or symbols from a distance and converting the results to a fraction.
On that note, regular eye exams are essential to keep your eyes’ health in check and update your prescription if you have one.
To assess the perception of 3D objects, the stereo test is utilized. This test measures an individual’s ability to detect depth and spatial relationships in a three-dimensional environment.
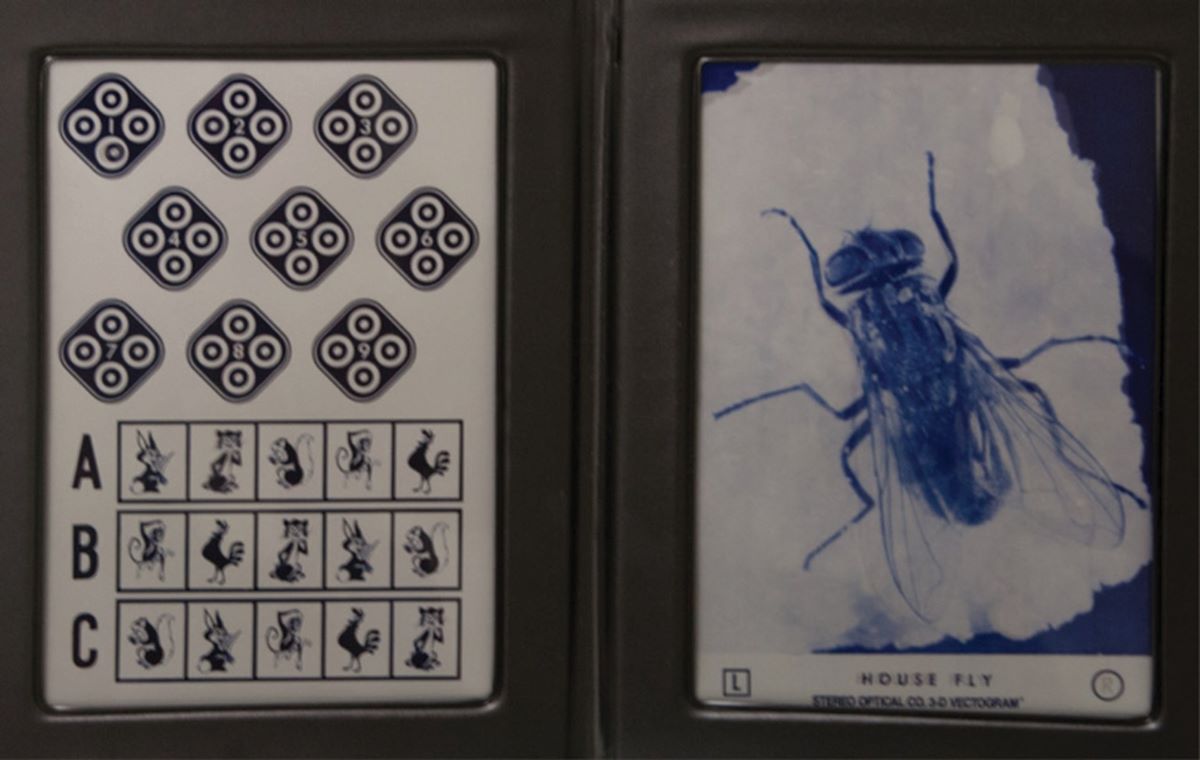
3. Randot Stereotest
The Randot Stereotest gauges how well you can see the depth and 3D structure in an image. It does this by showing you two pictures with random dots, which you look at through a special viewer. How well you can make out the 3D image from the 2D dots will determine your result.
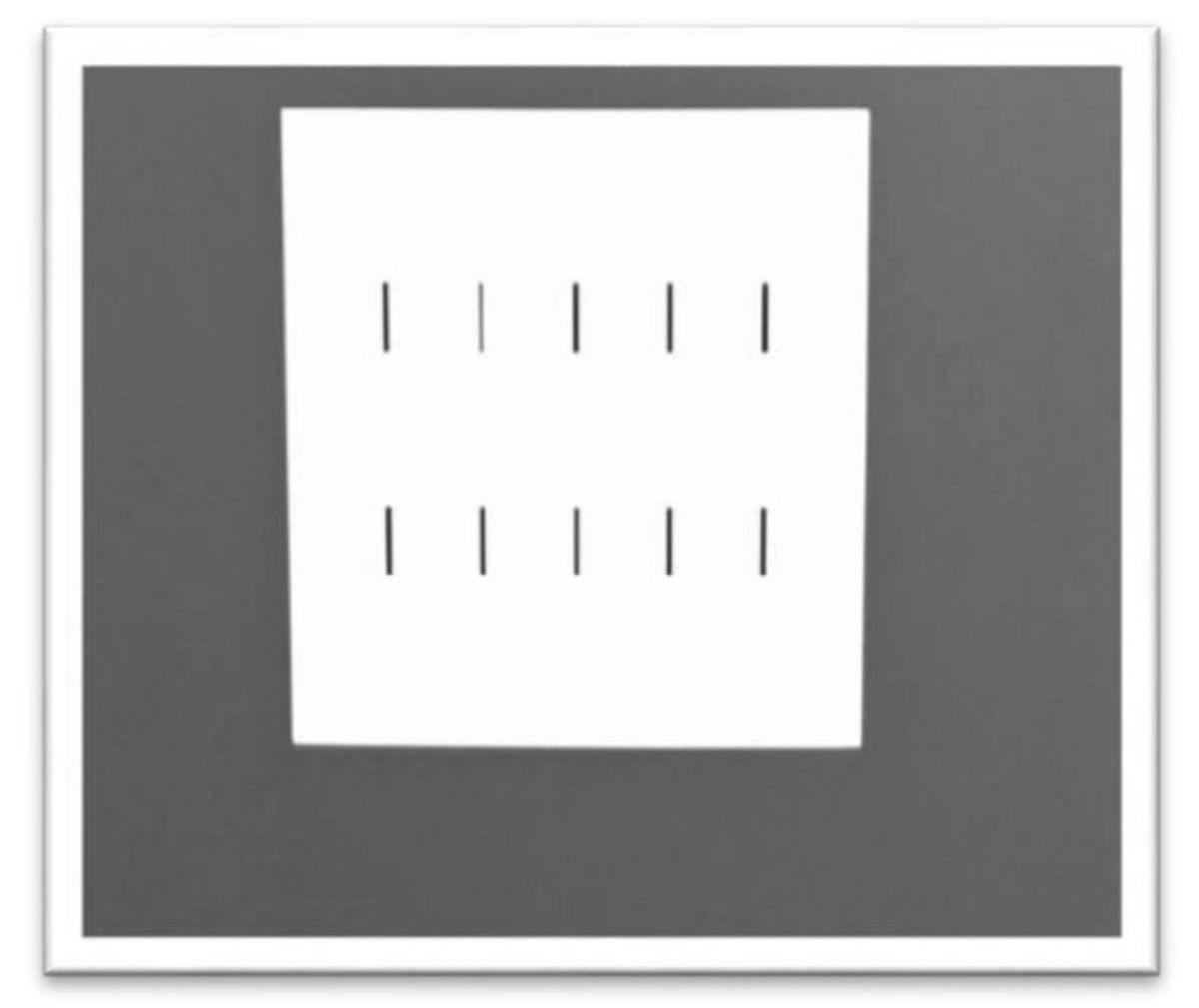
4. Contour Stereotest
The Contour Stereotest checks a person’s depth perception and looks for problems with stereo vision or binocular function. It works by making one wear glasses that make lines on cards appear 3D by gradually reducing the distance between the lines.
Are there vision issues that can affect depth perception?
Blurry vision
Blurry vision affects how well you can see the details of things and how far away they are. It makes it hard to focus on objects, so you can’t tell how close or far away they are.
This can make it hard to do tasks that require spatial awareness, such as playing basketball.
Strabismus (crossed eyes and lazy eye)
Strabismus is a condition where one’s eyes don’t point in the same direction. This can lead to double vision, trouble tracking moving objects, and other issues.
Since the brain can “rewire” itself during childhood, it’s crucial to catch and treat this condition early. Early treatment may restore normal binocular vision and prevent more serious vision problems down the line.
Amblyopia
Amblyopia is a condition where one eye’s vision does not develop properly in childhood, and is caused by the brain receiving different messages from each eye. It can cause difficulty seeing things far away, more accidents, and a lack of depth perception.
Eye trauma
Eye trauma is any injury caused to the structure surrounding the eyes, such as eyelids or the muscles controlling movement. Depending on the severity and location of the damage, it can result in blurred vision, double vision (diplopia), reduced vision, visual field loss, color vision loss, and affected depth perception.
Treatments & ways to improve depth perception
While some treatments and techniques require low levels of intervention and can be done at home, others require professional advice from an eye doctor.
Eye exercises
Doing regular eye exercises can help improve one’s vision by strengthening eye muscles, which leads to more accurate information from the eyes to the brain. Examples of eye exercises include following a moving object with your eyes and alternating between looking at near and far objects.
Improved lighting
Lighting can help improve depth perception by providing additional visual cues to the brain, such as details on an object, shadows, and edges.
Glasses or contact lenses
Corrective lenses can help improve depth perception by correcting any underlying vision problems that caused it in the first place, like blurry vision.
Corrective lenses can be used in two forms: eyeglasses and contact lenses. Before you decide on one, understand first the benefits and drawbacks of each type. It’s also best to consult an ophthalmologist or optometrist to determine which type of corrective lenses best suits your individual needs.
Vision therapy
Vision therapy, also known as visual training or eye therapy, uses specific exercises and activities to improve the brain’s ability to process visual information. It is typically done under an optometrist or ophthalmologist’s supervision.
Surgery
In some cases of more severely impaired depth perception, surgery may be required.
Strabismus surgery, also known as eye muscle surgery, corrects misaligned eyes. The procedure involves adjusting the muscles around the eye that control its movement by strengthening or weakening them. This helps to realign the eyes so that they point in the same direction, improving the patient’s vision and depth perception.
People with age-related, traumatic, congenital, or secondary cataracts may need to have cataract surgery. This procedure removes a cataract (or cloudy lens) that is affecting vision. It’s replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) that caters to the patient’s visual needs.
Aside from the natural lens becoming cloudy over time, cataract surgery may also be required to fix an injury to the eye, congenital defects, or medical conditions such as diabetes.
Corneal refractive surgeries like LASIK, PRK, or SMILE can also improve depth perception by correcting refractive errors such as myopia (shortsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism.
The importance of depth perception in our lives
Depth perception is like a superpower for our eyes. It helps us understand how far away things are and where they are in space. It’s vital for many daily activities, like throwing a ball, driving a car, and even walking around without bumping into things.
However, things can go wrong sometimes. If you’re having trouble with depth perception, please schedule an appointment with a trusted optometrist or ophthalmologist as soon as possible.

Written by:
Angie Garcia