How Do 3D Glasses Work?
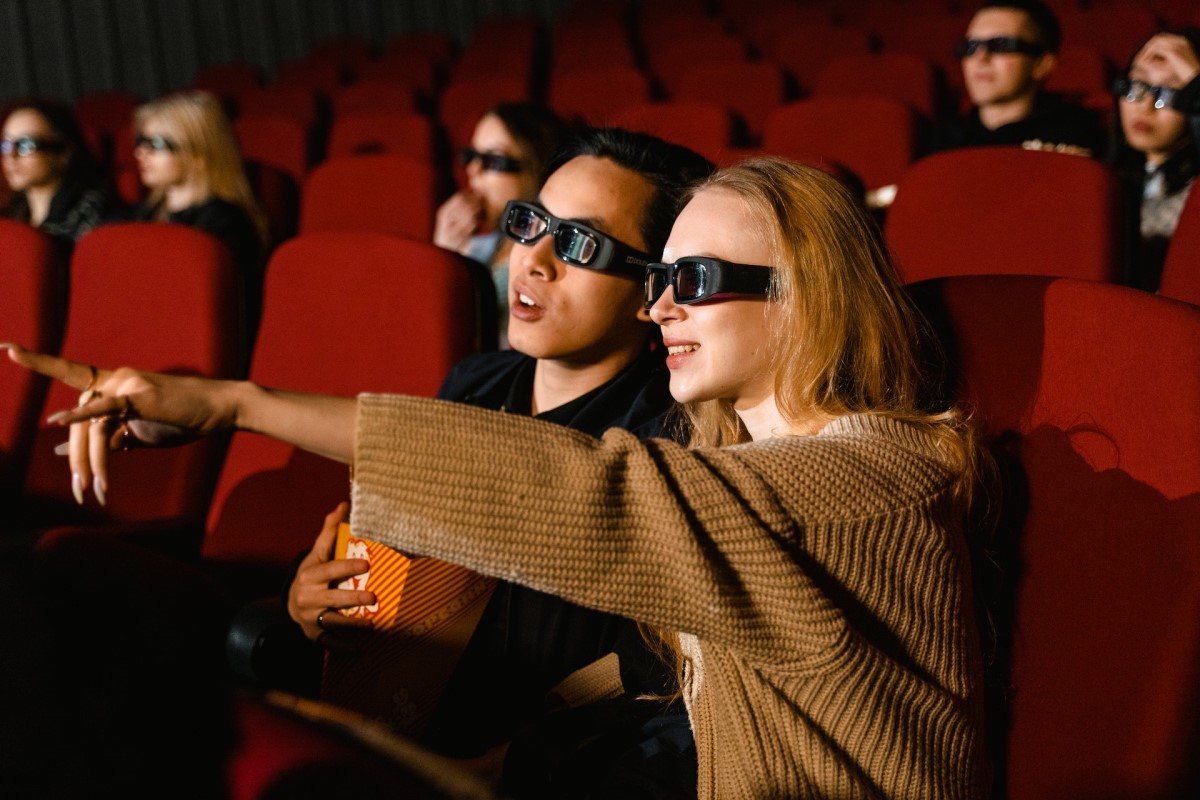
If you’ve ever been to a movie theater to watch a 3D movie, you’ve probably experienced that feeling of wonder from seeing scenes onscreen pop out for the first time. But have you ever wondered about the science behind this phenomenon?
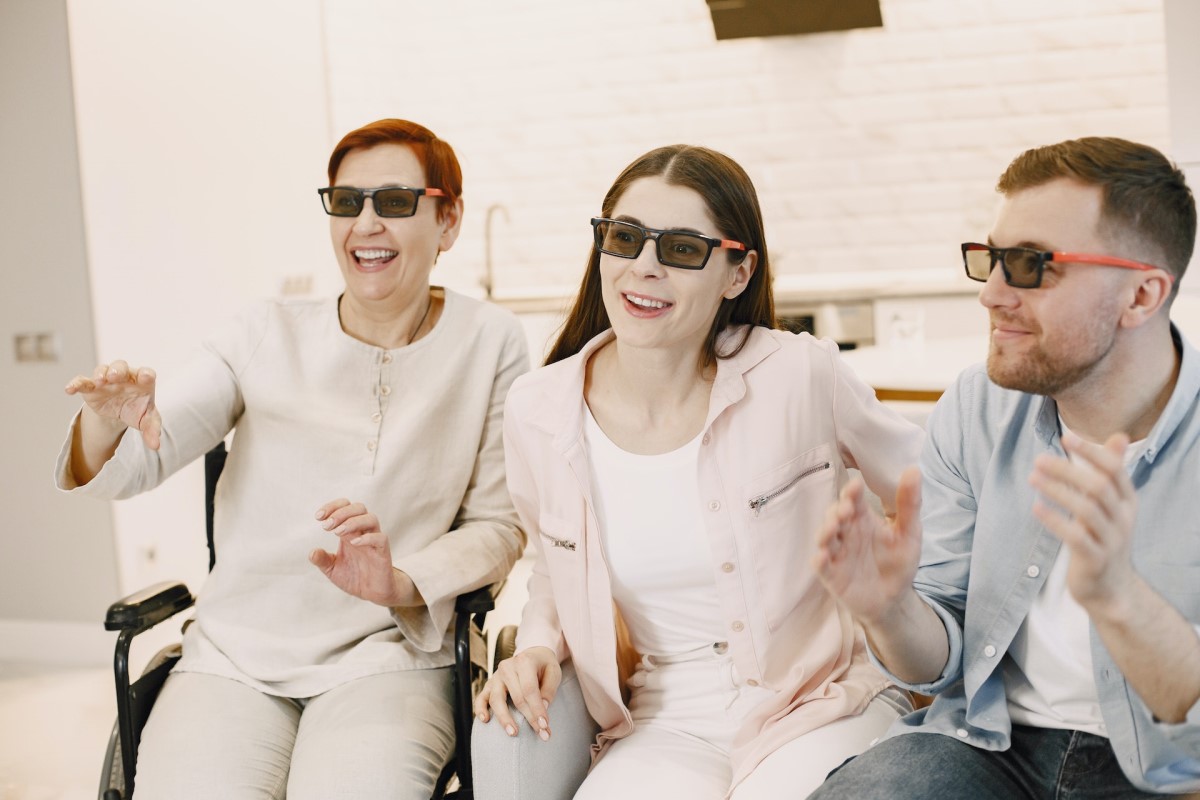
3D or stereoscopic glasses are what make this phenomenon possible by creating the illusion of depth in 3D movies, TV shows, and other content. They use stereoscopy, which involves presenting slightly different images to each eye. The brain then combines these two images into 3D, creating a lifelike viewing experience.
Today, we’ll explore the science behind 3D glasses and the different types available. Let’s take a closer look at the magic that brings movies and TV shows to life!
What are the types of 3D glasses?
Each type of 3D glasses has its own method to create the illusion of depth and enhance your viewing experience. They include polarized glasses, anaglyph glasses, and active shutter glasses, and each type has its own way of separating the left and right images to create the 3D effect.
By understanding the differences between these types of glasses, you can choose the best option for your needs and enjoy a more immersive 3D experience.
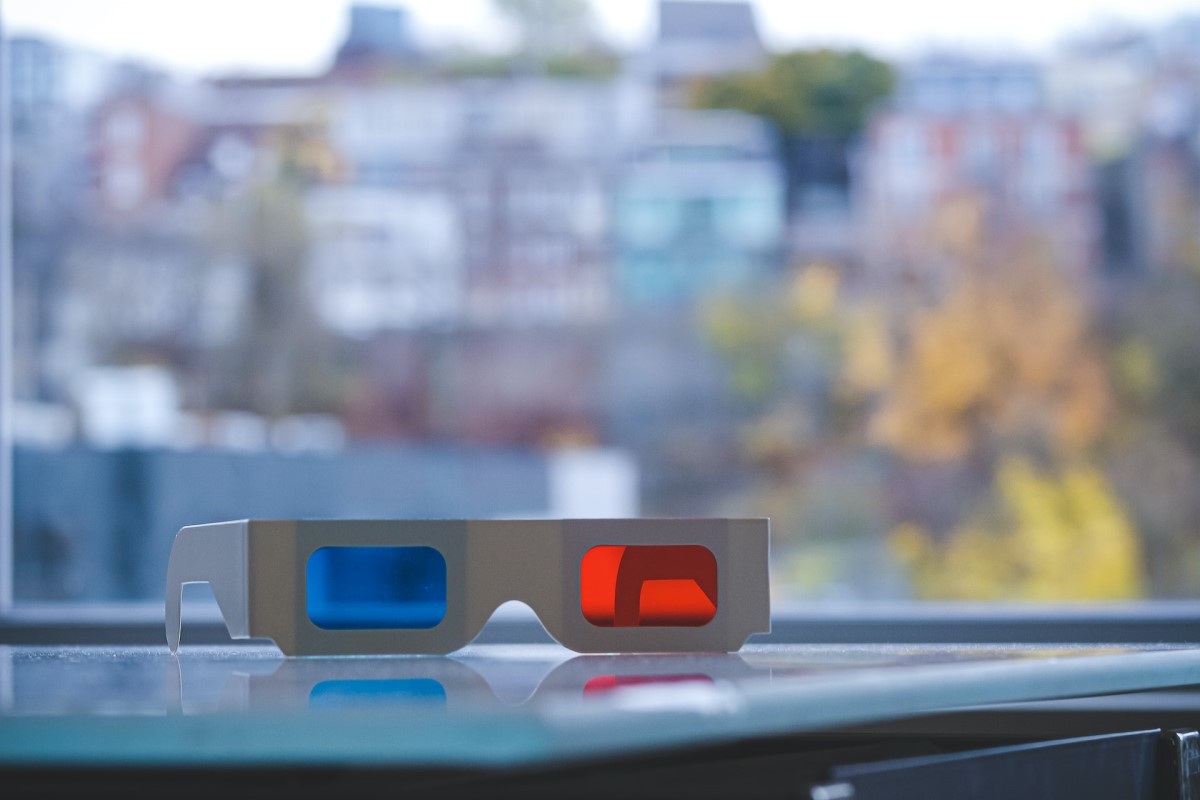
Anaglyph 3D glasses
Anaglyph 3D glasses are the oldest type of 3D glasses and have been around since the 1950s. They’re often used for low budget 3D applications and are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of 3D glasses.
They are also the oldest type of 3D glasses, having lost popularity over the years due to their limited color accuracy and uncomfortable wear.
Polarized glasses
Polarized glasses, on the other hand, are commonly used in movie theaters and considered to be a more mainstream form of 3D technology. They offer a more natural and comfortable viewing experience compared to anaglyph glasses and provide better color accuracy. However, they typically cost more than anaglyph glasses.
Shutter 3D glasses
Active shutter 3D glasses are the most advanced type of 3D glasses and are used in high-end 3D applications such as home theater systems and high-end gaming systems. While they offer the most immersive 3D experience, they’re the most expensive type of 3D glasses and require a compatible display device to work properly.
How do 3D glasses work?
How anaglyph glasses work
Anaglyph glasses achieve the 3D effect through color filtering, which means they use different colored lenses to block out light waves. The red lens filters out all colors except for red, and the blue lens filters out all colors except for blue.
This means that each eye sees a slightly different image, with the red lens blocking out the blue-tinted parts of the left image and the blue lens blocking out the red-tinted parts of the right image. Your brain then combines these two images into a single 3D image.
Anaglyph glasses can be used with almost any display but tend to produce a lower-quality 3D image with reduced color accuracy.
What about polarized glasses?
Polarized glasses use light polarization to achieve a similar effect, which means each lens is tuned to block out a certain orientation of light waves.
The 3D movie projector or display is set up to simultaneously project two slightly different images, which create the illusion of depth and trick the brain into perceiving a three-dimensional image.
When you put on the polarized glasses, the lenses filter out the light waves that are not oriented in the correct direction for each eye, allowing each eye to see a slightly different image. Your brain then combines the two images into a single 3D image, creating the illusion of depth.
Compared to anaglyph glasses, polarized 3D glasses provide a higher quality 3D experience with less color distortion. However, this varies depending on the screen they’re paired with and can result in limited viewing angles.
How active shutter glasses work
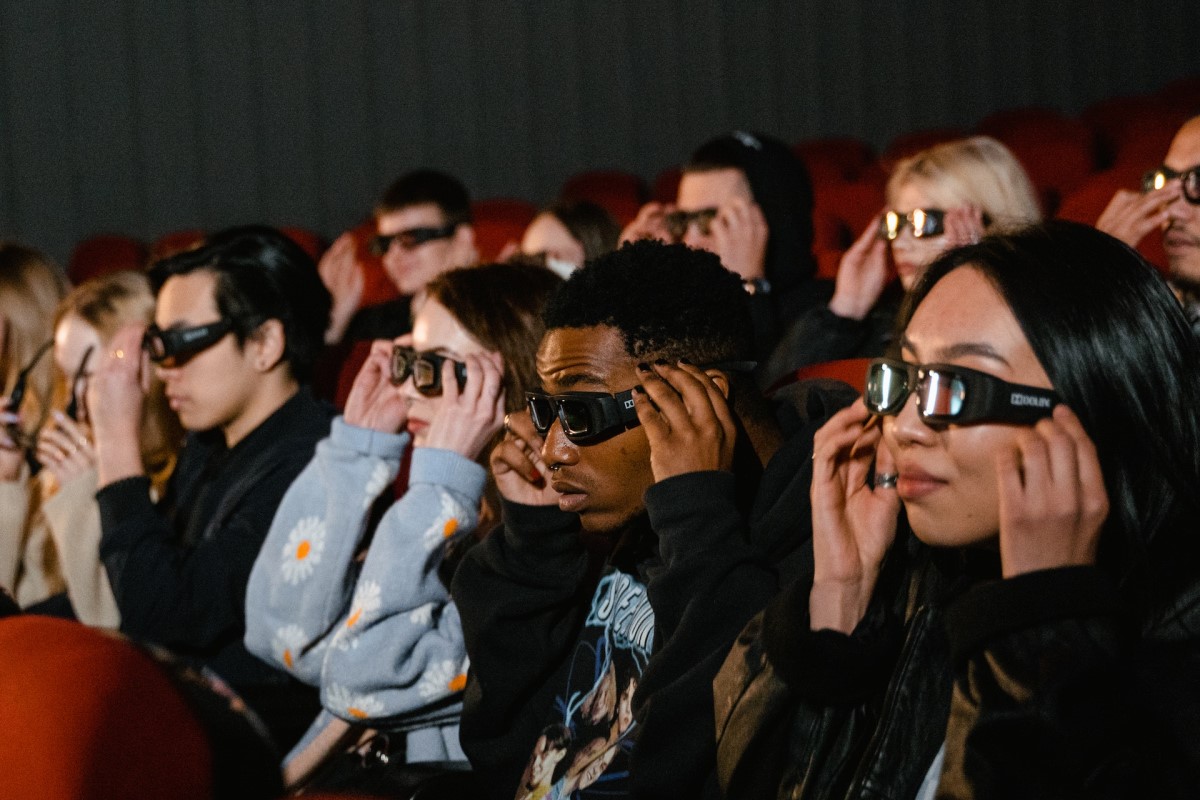
Active shutter glasses use shutter technology to rapidly block and unblock the lenses, creating a flickering effect that allows each eye to see different images.
Their ability to do so comes from their synchronization with the TV or display, as well as having liquid crystal lenses that rapidly open and close in time with the images on the screen. When the left image is displayed, the lens of the glasses opens up and lets the image through while the right lens remains closed.
When the right image is displayed, the right lens opens up, and the left lens closes. The process happens so quickly, at a rate of around 120 times per second, that the viewer perceives a single 3D image.
Out of the three types, active shutter glasses can provide arguably the most high-quality 3D experience with good image quality and minimal crosstalk, which is when the left and right images “bleed” into each other and the 3D effect is diminished. However, active shutter glasses can be more expensive than other 3D glasses, and some people may find the flickering effect uncomfortable or distracting.
Generally, when we look at an object in the real world, each eye sees a slightly different image of that object because they are positioned at different angles. Eyes are complex and hardworking organs that allow us to process visual details and understand our surroundings.
Our brain combines these two images into a single three-dimensional image, which gives us a sense of depth and spatial awareness.
3D glasses mimic this natural process of seeing things in the real world. They present a slightly different image to each eye, which tricks the brain into perceiving depth and creates the illusion of a three-dimensional image.
Have there been any advancements in 3D technology?
Recent years have seen significant advancements in 3D technology, including those in displays and glasses.
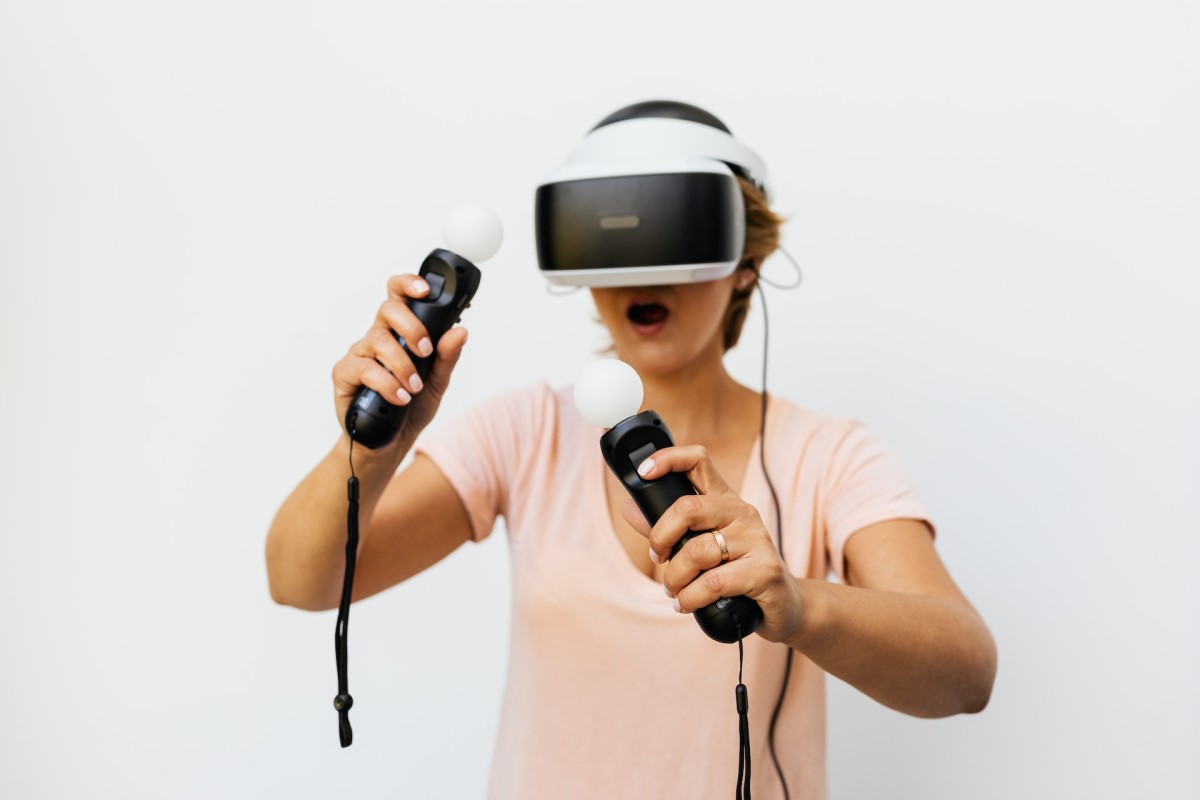
These innovations are leading us to a new era of higher quality and more immersive 3D experiences. For example, virtual reality (VR) headsets are becoming more advanced and accessible. Imagine being fully transported into a virtual world, where you can interact with digital environments and objects just as you would in the real world.
Despite these advancements, there are still limitations to current 3D technology. For instance, some people may experience discomfort or headaches while wearing 3D glasses or virtual reality headsets. Certain displays require us to view something from a specific angle or distance to get the full 3D effect.
Other interesting applications of 3D glasses
3D glasses are more than just a fun accessory for movie-goers. As mentioned above, 3D glasses have been combined with VR to take gaming to the next level by creating a fully simulated environment that surrounds the user, allowing for more realistic interactions and engagement.
In the medical field, 3D glasses are used to create detailed 3D models of the human body, aiding in the accurate diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions. And in scientific visualization, 3D glasses help researchers and scientists better understand complex phenomena.
With 3D technology progressing at a faster rate than ever, the possibilities for 3D glasses continue to expand.
Imagine a future where 3D glasses are no longer just a movie-watching accessory, but a way to transform the way we experience the world around us.
Imagine diving into virtual reality gaming, exploring the depths of the ocean through an educational documentary, or even experiencing a live concert like never before. The possibilities are truly endless with the advancements being made in 3D technology.
The exciting potential of 3D eyewear
As you can tell by now, there are so many cool things we can do with 3D glasses beyond just entertainment.
From medical imaging to scientific visualization, 3D glasses basically have the potential to revolutionize our perception of the world around us. As technology evolves, it will be fascinating to see how 3D glasses develop and become more integrated into our daily lives.
The future is bright for 3D glasses, so keep an eye out for the latest advancements and be ready to experience the world in a new way!

Written by:
Angie Garcia