How Far Can the Human Eye See?
Have you ever gazed at the endless sky and wondered just how far you can see with your own eyes? Or have you ever trekked to the peak of a mountain just to get a panoramic view?
Knowing how far the human eye can see is crucial to understanding our own visual capabilities and limitations. Whether it’s taking in the breathtaking panorama of a mountain range or simply spotting your car in a crowded parking lot, our eyes play a vital role in our daily experiences.
If you’ve always wanted to know how far the naked human eye can actually see, you’ve come to the right place. Read on to find out more.
Is there a limit to how far our eyes can see?
To keep it short, the human range of vision is infinite.
If you’re wondering how far you can see into the horizon from merely standing (assuming you have an average height of five feet), you will be able to see things as far as three miles before Earth curves out beneath your view. If you rent a room on top of a 10-story building, you’ll be able to feast your eyes on the cityscape for as far as twelve miles into the horizon.
If you’d rather see the world on top of a mountain, especially if it’s on top of the tallest mountain on earth, Mt. Everest, you’ll get a panoramic view spanning two hundred miles into the horizon before your vision is obstructed by the earth’s curvature. Depending on the height of the mountain, it’s even possible to see as many as dozens of cities in the distance.
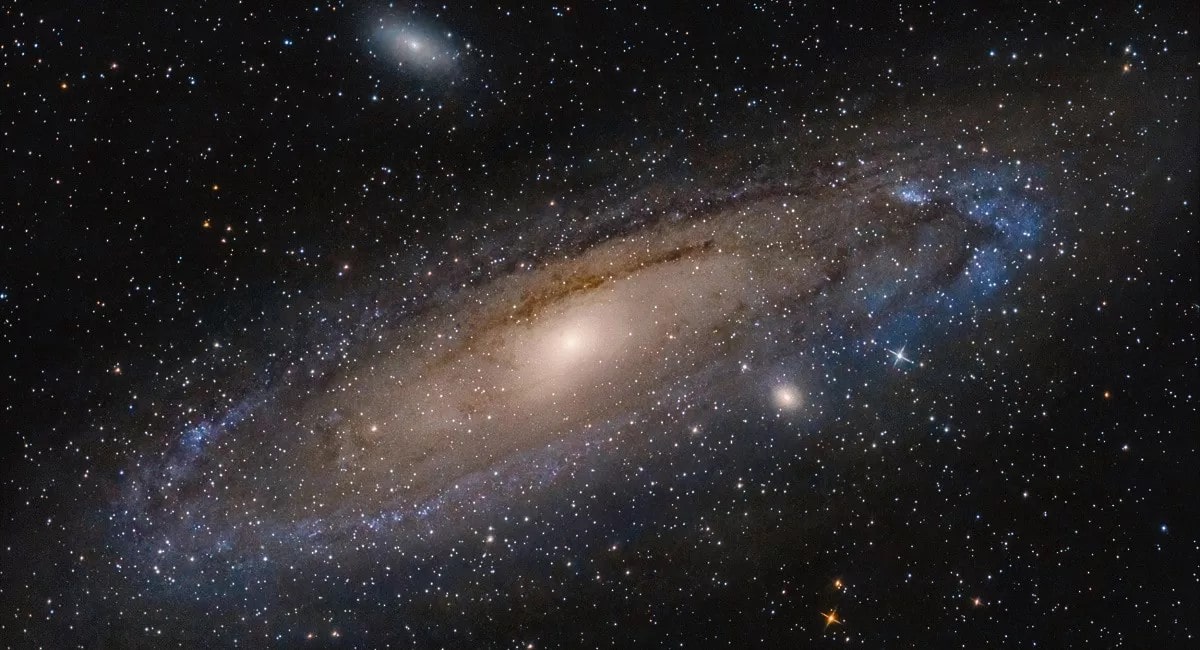
Needless to say, you’d be able to see even farther if your line of sight isn’t obstructed by the earth’s curvature. For instance, if you gaze up at the star-filled sky, you’ll be able to see the Andromeda galaxy, which is 2.5 million light-years away from us. In fact, it’s the farthest that our naked eye can see.
From stars in the night sky to the distant Andromeda Galaxy, the human eye can see some truly awe-inspiring things, but what determines the limits of our vision?
What factors affect how far we can see?
Your eyes have the potential to see things from seemingly limitless distances, but whether or not you actually can is influenced by a variety of factors, such as the health of your very own eyes, the size and brightness of the objects themselves, and the obstructions along your line of sight.
The health of your eye
The well-being of your eyes plays a significant role in how far you can see. An average person has a visual acuity of 20/20, which means you can see things clearly from 20 feet away.
However, conditions like nearsightedness and other common vision problems can limit your ability to see from a distance. To remedy these, go for regular eye exams. With your results, your eyecare expert can catch potential issues before they worsen, diagnose underlying conditions, and suggest the right corrective measures.
An object’s size and brightness
As you already know, larger objects are easier to see from a distance than smaller ones. Brighter objects are also more noticeable than those that are not as bright. This is why you can easily see the sun from far away on a clear day while finding it difficult to see things in the dark.
Because of their tremendous size and brightness, stars and galaxies can still be seen by human eyes in the night sky even if they are hundreds or thousands of light-years away.
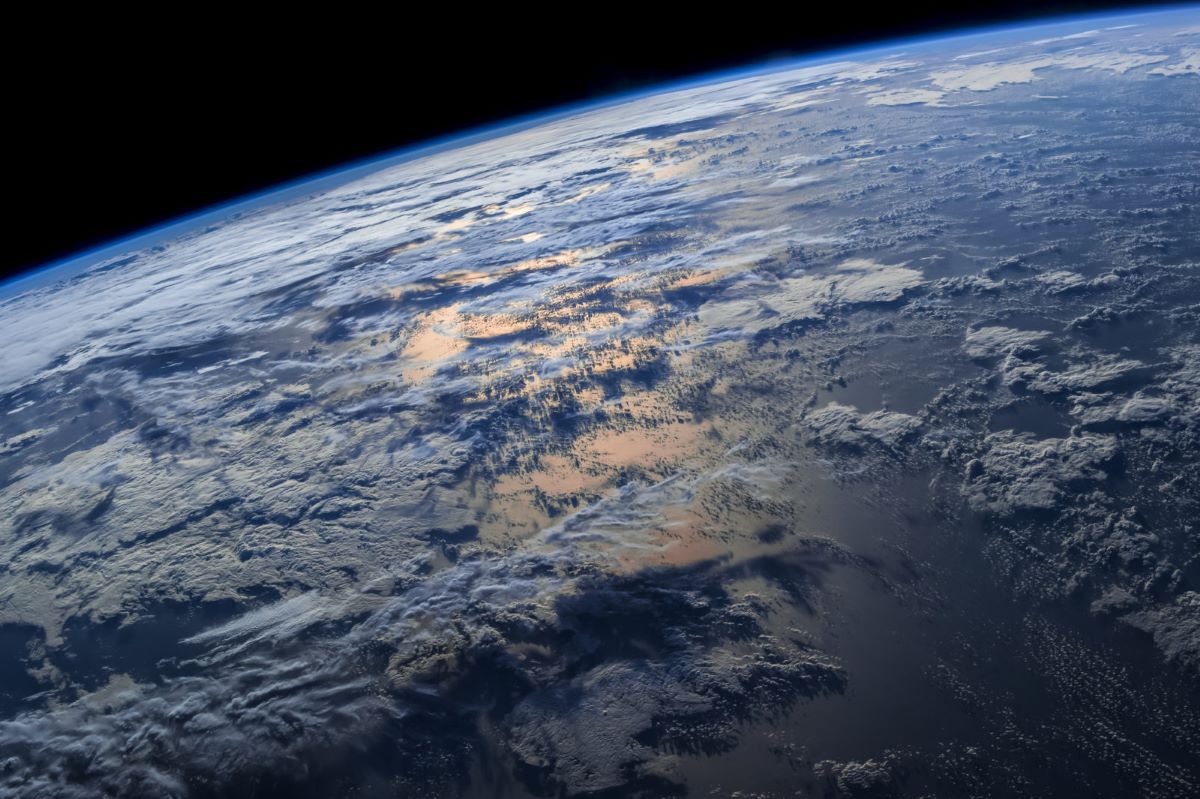
Earth’s curvature
Human eyes are capable of seeing incredible distances, but the view can sometimes be limited by the Earth’s curvature. As the Earth is a sphere, its curved shape means that the farther away you move from an object, the more it’ll gradually dip below the horizon and become hidden from view, typically around 8 inches per mile.
The angle from which you’re viewing also makes a difference. For instance, if you’re looking at a distant scenery from a high elevation such as a mountain, you’ll have a wider and more unobstructed view compared to when you’re looking at the same scenery from ground level.
Other obstructions in one’s sight line
Any obstructions in your line of sight can prevent you from seeing things that are further away. This could be anything from trees, buildings, clouds, or even people standing in front of you. Even dust, smoke, fog, and water vapor can hinder your ability to see further.
On a cloudy day, it may be easier to see large, bright objects like the moon, but harder to catch smaller, dimmer objects like stars.
Glare caused by bright lights being reflected off a flat surface can make it difficult to see objects as well.
Interestingly, research has found that, as long as there’s no obstruction in the sightline, the unaided human eye can see a candle flame from 1.6 miles away.
How does the human eye process images?
Eyes are like magic portals, capturing and transforming light into images that the brain can understand.
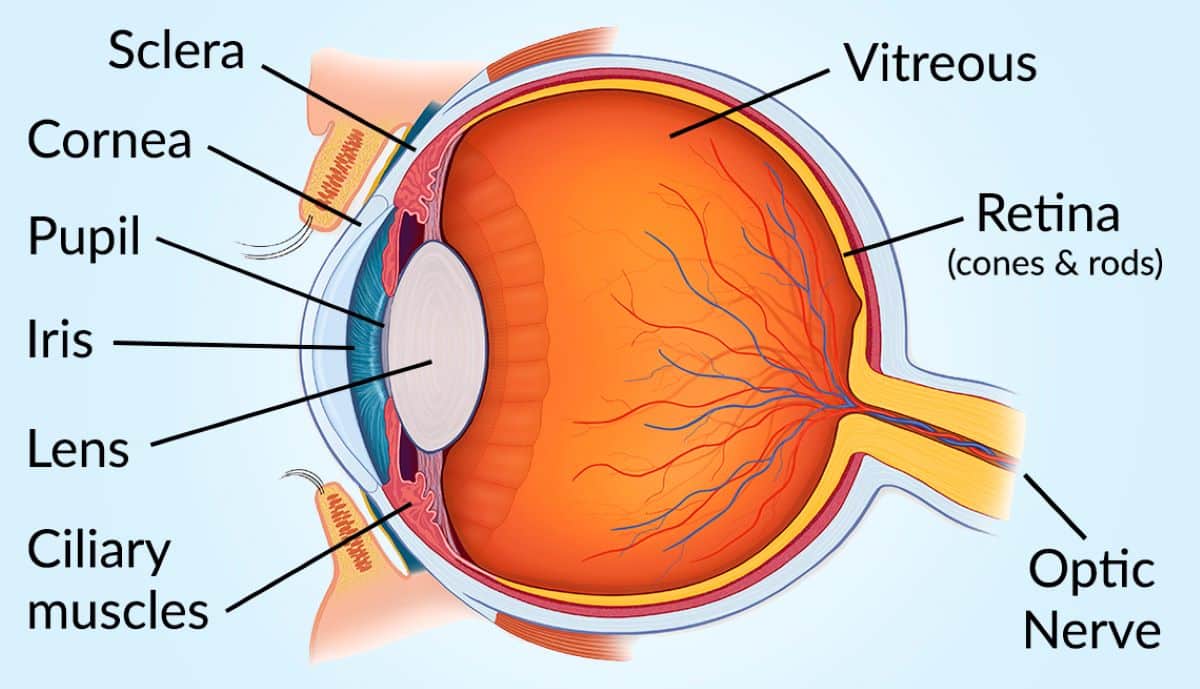
It all starts with the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye that helps guide the light and focus it directly onto the pupil.
The iris, that colored ring around the pupil, works like a camera shutter, controlling how much light enters the eye. This enables pupils to dilate in dimmer light and contract in bright light.
The lens then takes over, fine-tuning and adjusting the light so that you can see objects clearly, no matter how far away they are.
After that, the light reaches the back of the eye, or the retina – a thin layer of tissue that houses photoreceptors called rods and cones. These tiny cells transform the light into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain through the optic nerve.
From there, the brain works its magic, converting these signals into the images you see, and all this happens in the blink of an eye — pun fully intended.
Take care of your eyes & your eyes will take care of you
Keeping your eyes healthy is key to seeing and enjoying the world in all its beauty. From magnificent sunsets to the rolling hills in the distance, our eyes are our window to the world.
To make sure you can see as much of the world as possible, practice healthy habits and get your eyes checked on time. They deserve the same amount of care and attention that you put into every other part of your body.

Written by:
Shu Kie