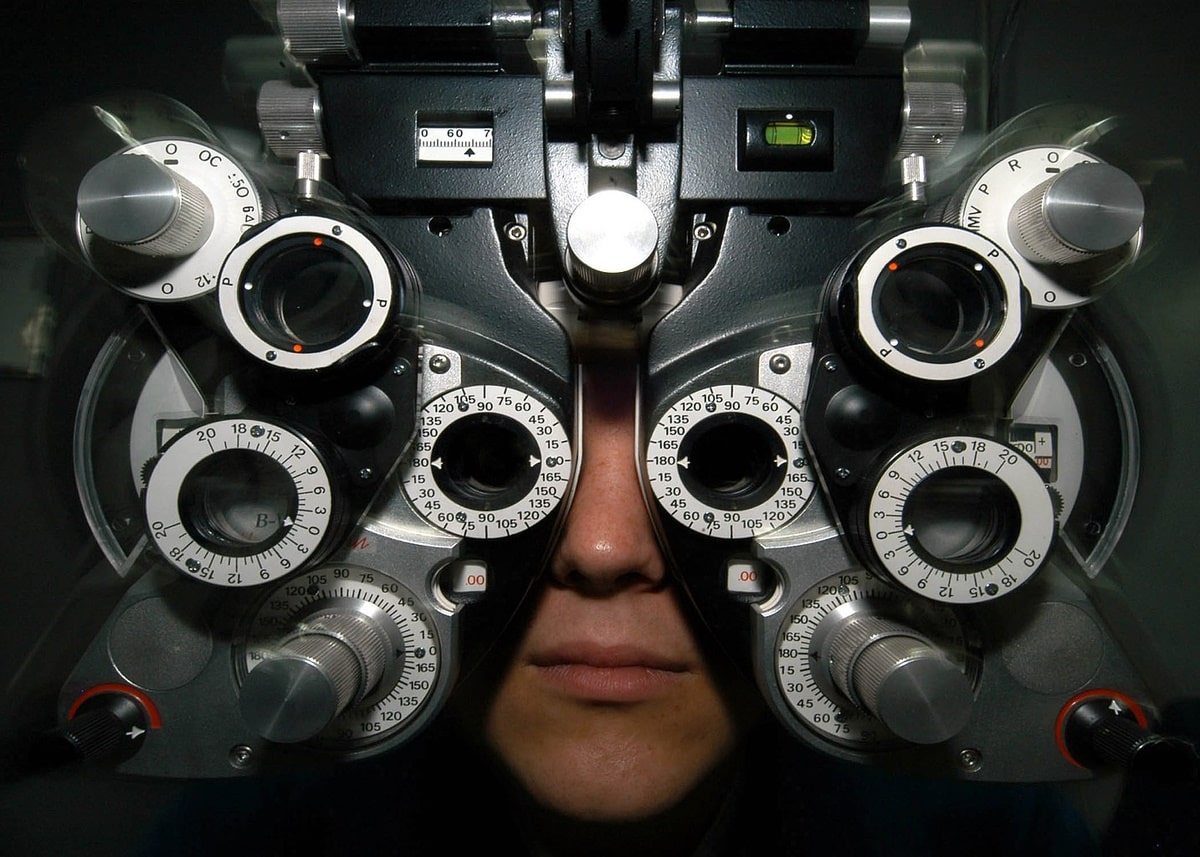
The Phoropter: An Essential Tool for Eye Exams
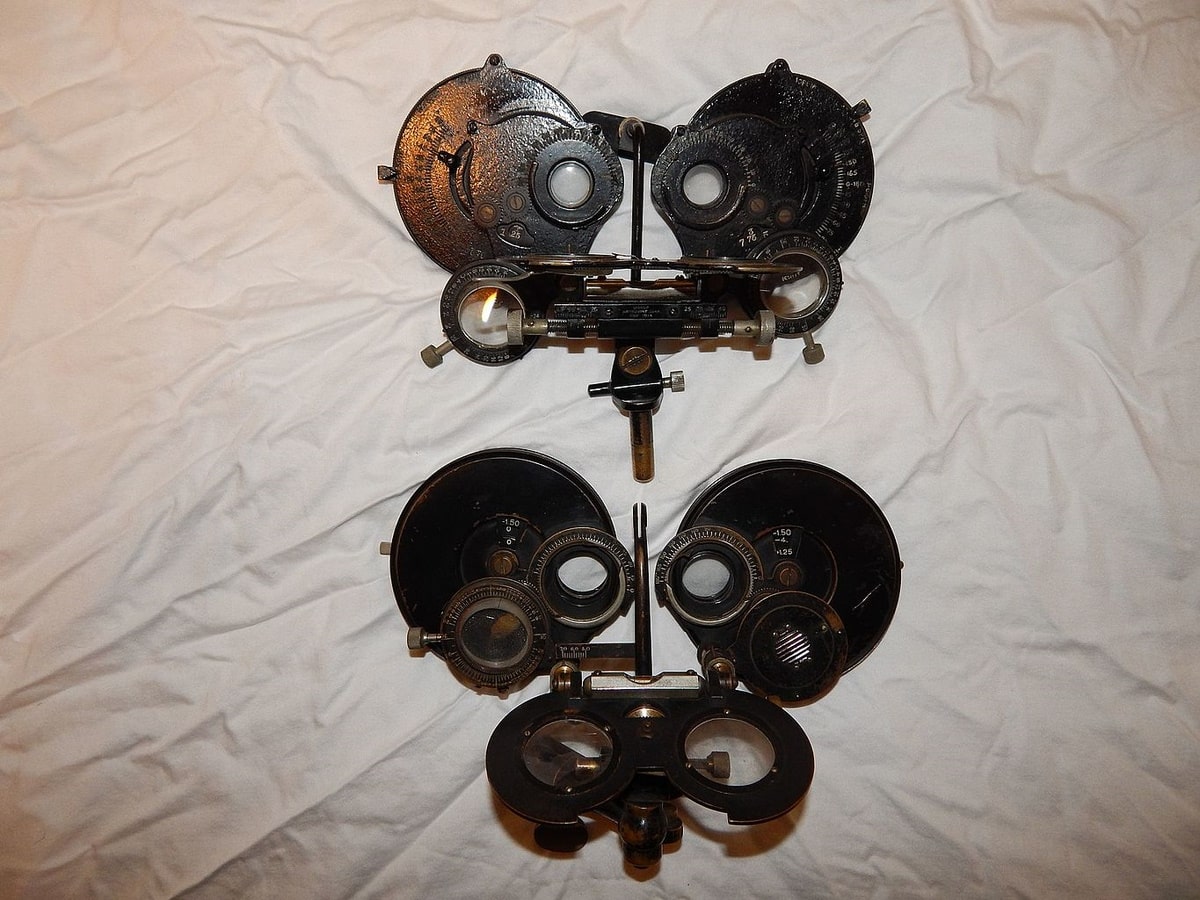
The phoropter, an eye test instrument that appears like an odd-looking robot mask invented in the early 1900s, remains an essential asset in the eye care industry, particularly for eye exams or vision testing procedures called refraction.
A marvel of engineering, the phoropter helps eye care specialists to know one’s refractive errors and determine the appropriate prescription for correcting vision.
What is a phoropter?
The phoropter device is one of several refractors or optical telescopes. It enables ophthalmologists and optometrists to determine vision issues. For example, it can help diagnose nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia.
A few other refractor types are autorefractor, keratometer, retinoscope, and aberrometer. Each instrument has its strengths and limitations. Selecting the right one depends on the particular needs of the patient and the preferences of the eye care professional.
The phoropter instrument consists of cylinders, prisms, and lenses that measure the eye’s refractive error to help decide on an eye prescription. It can also measure the eye’s natural resting position, near-distance focal ability, binocular vision, and eye movements.
An eye care professional uses the phoropter to modify the power and orientation of the lenses a patient is testing.
How does a phoropter work?
An optician places a phoropter in front of a patient’s eyes. The patient is subject to a series of lens choices. The eye care professional eventually reaches a final eyeglass prescription through visual trial and error. Much of the process relies on the patient’s answers in identifying letters or images on a chart.
In addition to its refraction functions, the phoropter can also help calculate binocular vision, referring to a patient’s capacity to utilize both eyes in unison and to scrutinize one’s capability to concentrate on objects situated at varying distances.
What the phoropter can and can’t do
While a phoropter is essential in determining a patient’s prescription for corrective lenses, there are certain limitations to what it can do. For example, it cannot diagnose eye diseases, assess eye health, or substitute a comprehensive eye exam. Below are the details of a phoropter’s scope of functions and limits.
What a phoropter can do
- Measure refractive errorThe phoropter can help determine the correct prescription for corrective lenses, allowing an eye doctor to know the degree of nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism a patient has.
- Test visual acuityThe phoropter can help test visual acuity or how well a patient can see at different distances, which is necessary to assess one’s vision and determine the appropriate corrective lens prescription.
- Determine binocular visionThe phoropter can help assess how well a person’s eyes work together, essential for evaluating overall vision health.
- Assess accommodative functionWe can also use a phoropter can also be used to evaluate how well a patient can focus on objects at different distances, which is essential for diagnosing specific vision problems.
What a phoropter can’t do
- Diagnosing eye diseasesThe phoropter is not meant for diagnosing eye diseases or conditions, like glaucoma or macular degeneration, which require other instruments like an ophthalmoscope or slit lamp.
- Assess eye healthIt’s impossible to diagnose eye health issues such as dry eye or corneal irregularities using the phoropter. These require other instruments, such as a corneal topographer or keratometer.
- Substitute a comprehensive eye examAlthough a phoropter can provide valuable information on a patient’s prescription for corrective lenses, it cannot substitute a comprehensive eye exam meant for a complete assessment of a patient’s overall eye health and function. An eye doctor may perform other tests and evaluations to ensure the patient’s eyes are healthy and functioning correctly.
History and evolution of the phoropter
The phoropter was invented in the early 1900s, with Nathan Shigon creating the Ski-optometer, later followed by Henry DeZeng with his Phoro-optometer. Refraction began with jewelers bringing eyeglasses door-to-door for folks to try on and purchase.
From refraction’s beginnings in 1909 to almost four decades later, the redesigned refractor system, the RxMaster, introduced in 1956, became the archetype for modern phoropters. The phoropter has since developed to measure refractive errors, including traits of binocular vision that refer to how well the eyes work together, to name a few.
Like most inventions over time, the phoropter has evolved into a more advanced, efficient system: the digital refractor.
According to ophthalmic supplies and services company Veatch Ophthalmic Instruments, modern digital refractors, in many ways, are the same as traditional manual phoropters in that they use the same methods to check and verify a patient’s optical prescription with cylinders, prisms, and lenses. However, digital systems offer far more functionality, which makes refraction exams more streamlined, accurate, and effortless than ever.
Veatch explained: “From pretest data to the final prescription, doctors no longer have to enter data into the refractor and patient’s records manually. Instead, each piece of equipment communicates with the others with a digital system.
Pretest data automatically moves to the refractor. All subsequent information is saved directly into the patient’s digital record. This system eliminates repetitive entries and makes prescription checks and updates easy and organized.”
Who makes the best phoropters?
Over a century since its invention, the phoropter’s market size has reportedly increased and is estimated to reach US$139.21 million by 2028. Key players in the phoropter industry include:
- Briot
- Essilor
- Huvitz
- Marco
- Nidek
- Reichert
- Rexxam
- Righton
- Topcon
- Zeiss
The global phoropter makers are engaged in key market segments:
- Deployment type
- Digital phoropters
- End-user type
- Hospitals
- Manual phoropters
- Ophthalmic clinics
- Optometric clinics
Phoropter advancement remains vivid
In perspective, the phoropter continues to serve as an essential instrument in resolving eye vision problems for people worldwide. In addition to its success as eye care technology, the phoropter has also improved the understanding of treating common eye conditions.
Further advancements in the phoropter device remain exciting, with the potential to improve refraction exams, making them more streamlined, accurate, and effortless.

Written by:
Shu Kie